Definition
is a measure of the osmotic pressure gradient (as defined by the water potential of the two solutions) of two solutions separated by a semipermeable membrane. It is commonly used when describing the response of cells immersed in a external solution. Like osmotic pressure
tonicity is influenced only by solutes that cannot cross the
membrane, as only these exert an osmotic pressure.
Solutes able to freely cross the membrane do not affect
tonicity because they will always be in equal concentrations on both sides of the membrane.
Osmosis is most easily defined as the diffusion of water, and diffusion defined is the movement of
substances from a high to low concentration. While this sounds simple, osmosis has a profound
impact on the processes of the human body. Within the human body, cells live within a fluid
environment that can contain a combination of dissolved particles, such as salt and potassium. Cells
have a semi-permeable membrane that separates the intracellular fluid (inside the cell) from the
extracellular fluid (outside the cell). Diffusion and osmosis between intracellular and extracellular
fluids depend on the number and types of dissolved particles inside and outside of the cell.
A cell’s tonicity is dependent on this.
is a measure of the osmotic pressure gradient (as defined by the water potential of the two solutions) of two solutions separated by a semipermeable membrane. It is commonly used when describing the response of cells immersed in a external solution. Like osmotic pressure
tonicity is influenced only by solutes that cannot cross the
membrane, as only these exert an osmotic pressure.
Solutes able to freely cross the membrane do not affect
tonicity because they will always be in equal concentrations on both sides of the membrane.
Osmosis is most easily defined as the diffusion of water, and diffusion defined is the movement of
substances from a high to low concentration. While this sounds simple, osmosis has a profound
impact on the processes of the human body. Within the human body, cells live within a fluid
environment that can contain a combination of dissolved particles, such as salt and potassium. Cells
have a semi-permeable membrane that separates the intracellular fluid (inside the cell) from the
extracellular fluid (outside the cell). Diffusion and osmosis between intracellular and extracellular
fluids depend on the number and types of dissolved particles inside and outside of the cell.
A cell’s tonicity is dependent on this.
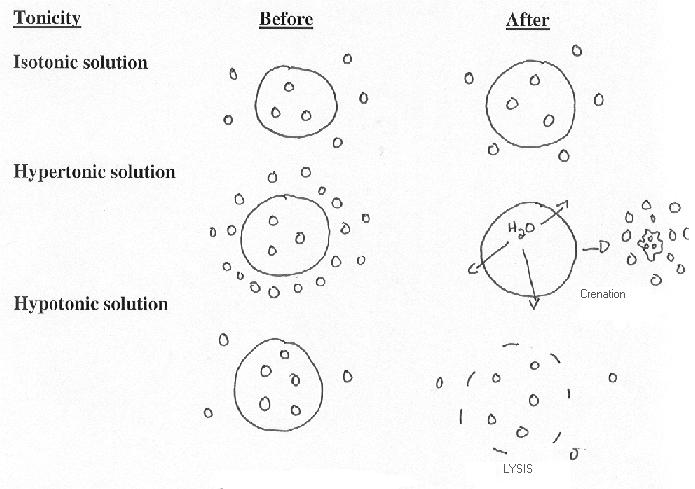
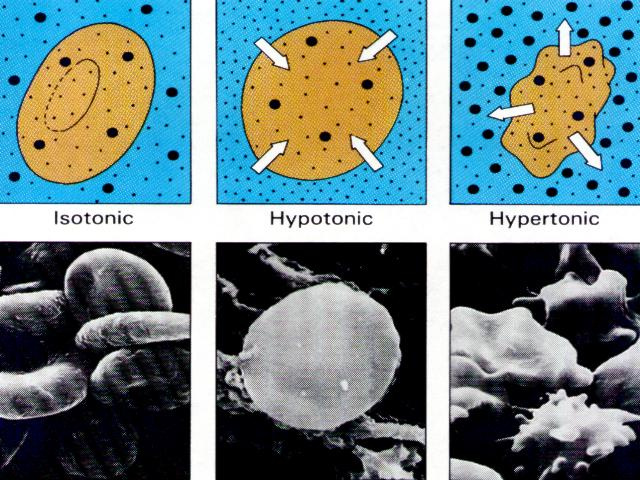
* There are three classifications of tonicity that one solution can have relative to another. The three are:
HYPERTONIC, ISOTONIC, HYPOTONIC
1- Hypertonicity:
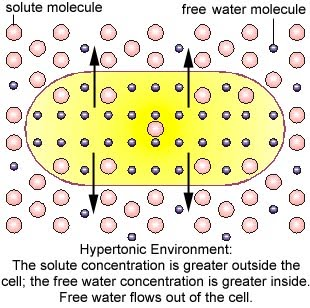
Hypertonic refers to agreater concentration. In biology, a hypertonic solution is one with a higher concentration of solutes on the outside of the cell. When a cell is immersed into a hypertonic solution, the tendency is for water to flow out of the cell in order to balance the concentration of the solutes.
When plant cells are in a hypertonic solution, the flexible cell membrane pulls away from the rigid
cell wall, but remains joined to the cell wall at points called plasmodesmata. The cell takes on the appearance of a pincushion, and the plasmodesmata almost cease to function because they become constricted: a condition known as plasmolysis. In plant cells the terms isotonic, hypotonic and hypertonic cannot strictly be used accurately because the pressure exerted by the cell wall significantly affects the osmotic equilibrium point.
Tonicity – Refers to the comparison of solute concentration between two solutions.
Hypertonic solution –[high solute][low water]
HYPERTONIC, ISOTONIC, HYPOTONIC
1- Hypertonicity:
Hypertonic refers to agreater concentration. In biology, a hypertonic solution is one with a higher concentration of solutes on the outside of the cell. When a cell is immersed into a hypertonic solution, the tendency is for water to flow out of the cell in order to balance the concentration of the solutes.
When plant cells are in a hypertonic solution, the flexible cell membrane pulls away from the rigid
cell wall, but remains joined to the cell wall at points called plasmodesmata. The cell takes on the appearance of a pincushion, and the plasmodesmata almost cease to function because they become constricted: a condition known as plasmolysis. In plant cells the terms isotonic, hypotonic and hypertonic cannot strictly be used accurately because the pressure exerted by the cell wall significantly affects the osmotic equilibrium point.
Tonicity – Refers to the comparison of solute concentration between two solutions.
Hypertonic solution –[high solute][low water]
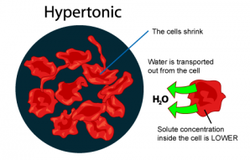
HOW IT AFFECTS ANIMAL AND PLANT CELLS
Animal Cells
In animal cells, being in a hypertonic environment results in crenation, where the shape of the cell becomes distorted and wrinkled as water leaves the cell. Some organisms have evolved methods of venting Hypertonicity; for example, saltwater is hypertonic to the fish that live in it. Since they cannot isolate themselves from osmotic water loss, because they need a large surface area in their gills for gas exchange, they respond by drinking large amounts of water, and excreting the salt. This process is called osmoregulation. An example of an animal cell showing the affects of hypertonicity is when your fingers wrinkle.
Animal Cells
In animal cells, being in a hypertonic environment results in crenation, where the shape of the cell becomes distorted and wrinkled as water leaves the cell. Some organisms have evolved methods of venting Hypertonicity; for example, saltwater is hypertonic to the fish that live in it. Since they cannot isolate themselves from osmotic water loss, because they need a large surface area in their gills for gas exchange, they respond by drinking large amounts of water, and excreting the salt. This process is called osmoregulation. An example of an animal cell showing the affects of hypertonicity is when your fingers wrinkle.
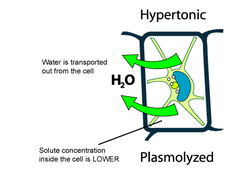
PLANT CELLS
When a plant cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, the water inside the cells are drawn out by osmosis. The vacuoles decrease in size. The cytoplasm also shrinks away from the cellulose cell wall and plasmolysis occurs. This causes a lack of structure for the plant and causes it to wilt, or become flaccid.
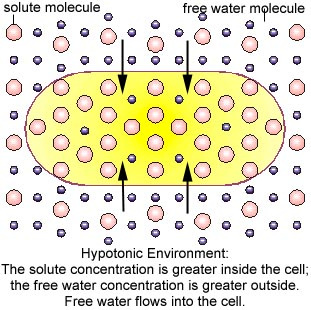
2- Hypotonicity
Hypotonic refers to a lesser concentration. A hypotonic solution has a lower concentration of solutes in its
surroundings, so in an attempt to balance
concentrations, water will rush into the cell, causing swelling. [2] Some organisms have evolved intricate methods of circumventing hypotonicity. For
example, saltwater is hypertonic to the fish that live in it. They need a large surface area in their gills in contact with
seawater for gas exchange, thus they lose water osmotically to the sea from gill cells. They respond to the loss by drinking large amounts of saltwater, and actively excreting the excess salt .This process is called osmoregulation. A hypertonic solution is used in osmotherapy to treat cerebral hemorrhage.[citation needed]
Hypotonic solution – [low solute] [high water]
When a plant cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, the water inside the cells are drawn out by osmosis. The vacuoles decrease in size. The cytoplasm also shrinks away from the cellulose cell wall and plasmolysis occurs. This causes a lack of structure for the plant and causes it to wilt, or become flaccid.
2- Hypotonicity
Hypotonic refers to a lesser concentration. A hypotonic solution has a lower concentration of solutes in its
surroundings, so in an attempt to balance
concentrations, water will rush into the cell, causing swelling. [2] Some organisms have evolved intricate methods of circumventing hypotonicity. For
example, saltwater is hypertonic to the fish that live in it. They need a large surface area in their gills in contact with
seawater for gas exchange, thus they lose water osmotically to the sea from gill cells. They respond to the loss by drinking large amounts of saltwater, and actively excreting the excess salt .This process is called osmoregulation. A hypertonic solution is used in osmotherapy to treat cerebral hemorrhage.[citation needed]
Hypotonic solution – [low solute] [high water]
HOW IT AFFECTS ANIMAL AND PLANT CELLS
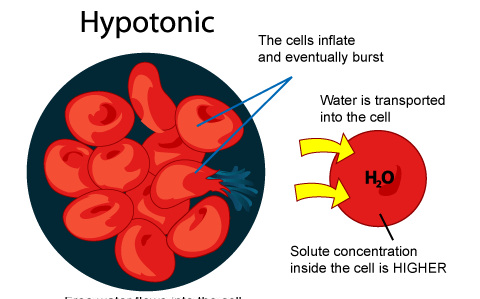
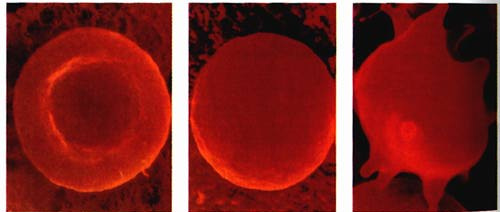
ANIMAL CELLS
In an animal cell, hypotonic solutions cause them to swell, they become bloated and triple their original size. By the time they have reached triple their size (how long this takes depends on each individual cell) they burst like a balloon and die.
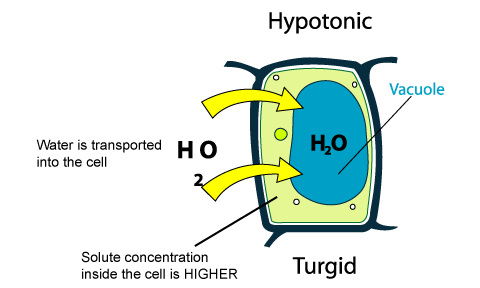
PLANT CELLS
When plants are placed in water, the water enters their cells (this is because their sap has a strong solution). The water enters the plant through osmosis and fills up the cell with water to its maximum capacity. A strong cell wall stops the cells from bursting (as in animal cells) and makes the plant to become turgid (becomes rigid/stiff because of water.)
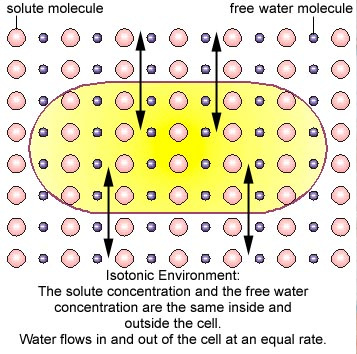
3- Isotonicity
An isotonic solution is one in which its effective
osmole concentration is the same as the solute
concentration of another solution with which it is compared.This occurs, for example, when the concentration of both water and total solute molecules are the same in an external solution as in the cell content. Water molecules diffuse through the plasma membrane in both directions, and as
the rate of water diffusion is the same in each direction that cell will neither gain nor lose water.
Isotonic solution – [same] of solute on both sides of membrane.
- Water will move from a hypotonic solution (environment) to a hypertonic solution (environment).
- No net movement of water will take place between isotonic solutions.
Tonicity Terms
refer to the concentration of solute in a solution not the concentration of water.
- No net movement of water will take place between isotonic solutions.
Tonicity Terms
refer to the concentration of solute in a solution not the concentration of water.
References
1-Sperelakis, Nicholas (2011). Cell Physiology Source Book: Essentials of Membrane Biophysics. Academic Press. pp. 288. ISBN 978-0-12-387738-3.
2-Definition — hypotonic". The Free Dictionary. Retrieved 23 August 2012.
WAS THIS INFORMATION USEFUL?

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed